Just imagine, how amazing it would be if we could predict the future. Hold this thought and imagine further how amazing it would be if we could predict the future prices of various financial assets and make money out of them. I am sure my last statement might have created some sort of excitement amongst you all. But the question remains of “How?” Well, there’s something known as derivative instruments in our financial market which can help us do this. But obviously, it’s not as easy as it sounds and as usual, I have got you covered! So, sit back as we unfold the complex world of the Derivatives market in the most simplified manner. Let’s get started!
What are Derivatives?
Derivatives are financial contracts that derive their value from the underlying assets. Confused? Let’s break it down one by one. A derivative instrument is a contract between a buyer and a seller based on their views about an underlying assets’ future price movement. An underlying asset can be any financial instrument like stocks, bonds, commodities, currencies, interest rates and even indices. So, the value at which this contract or derivative instrument is traded is based on the value of its underlying asset. For instance, in the case of a stock derivative say- RIL, the contract/derivative value will increase when RIL’s value increases. Note that you are trading a contract and not the underlying itself. Since its value is derived from an underlying (RIL from our example), this contract is known as a “Derivative instrument”.
History of the Derivatives market
Right from the Greek civilization to the present electronic trading, derivative instruments are believed to be present in the financial markets’ history for a long time. They are said to have existed in the cultures of Mesopotamia during the Greek civilization. Once, one of Aristotle’s followers named Thales, studying meteorology predicted that the olive crops would give a good yield that year. So, he went ahead and purchased all the olive produce around Athens even before they were harvested. As predicted by Thales, the olive produce turned out great and he made profits ahead with the help of derivative instruments.
What about the world’s largest economy, the US? In the 19th century, American farmers could not find buyers for their commodities. Later, they went ahead and formed the Chicago Board of Trade which evolved into the first-ever derivatives market dealing in standardized contracts. But where was India when the financial market was witnessing this essential change? Well, in the case of India, derivative instrument trading started in 1875 with the establishment of the Bombay Cotton Trading Association. There was a time post-independence when cash settlement and options trading was banned however, later it was uplifted with the creation of the National Electronics Commodities Exchange. And the rest is history.
What is the purpose of Derivatives?
Derivatives are primarily used for hedging and speculation purposes. Now, don’t get scared by these big words, I am here to make it easy for you.
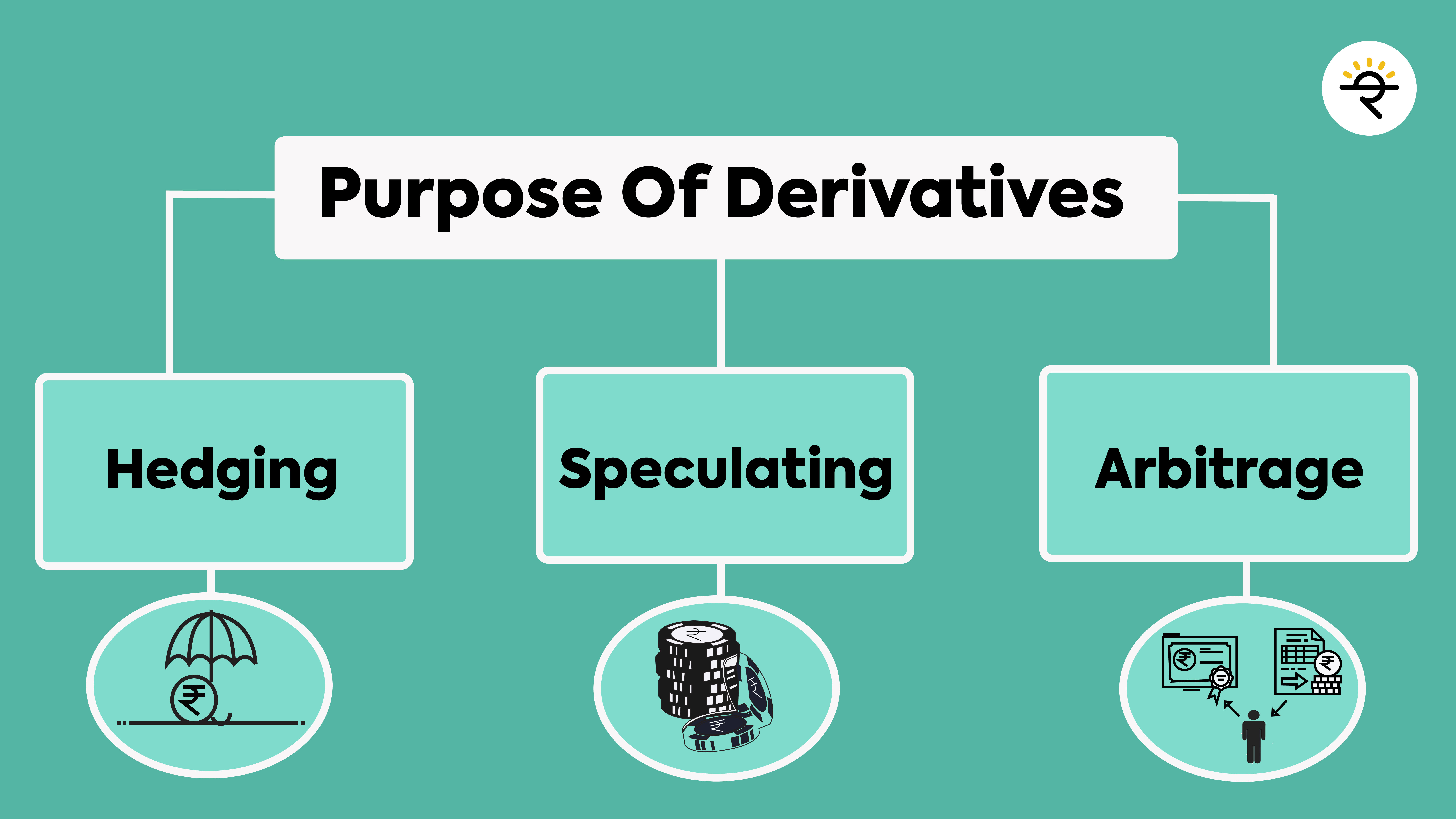
1. Hedging
To put it very simply for you, hedging means taking a position to limit your losses due to price fluctuations in the market. As derivatives are considered to be high-risk instruments, hedging plays an important role in minimizing the losses by taking an opposite position. This proves to be a good cushion for both investors and businesses to protect their portfolios during volatility.
2. Speculating
We all speculate about certain things on a daily basis. For instance, if you observe cloudy weather, you speculate that it will rain soon and hence carry an umbrella. Similarly, in the derivatives market, if you think the markets might go up and take a position accordingly then you are speculating. Speculating purely involves taking a position based on your views about an asset with an intent to generate profit. These are usually hunches or guesses based on the price movement. Unlike hedgers who try to minimize their risk, speculators try to make profits by taking a high risk.
3. Arbitrage
The main aim of arbitrage is to earn profits from the difference in the price of an asset in different market segments. It involves buying an asset from a market (say spot market) where the price is lower and simultaneously selling it on another market (say futures market) where it is trading at a higher price. Arbitrage involves relatively low risk. However, due to market efficiency theory, such opportunities can be hard to find.
Bottom line
Derivatives are often used by businesses that can be largely affected on an operational level due to fluctuating prices of certain commodities. This helps them to reduce their market risk and protects their bottom line. Retail investors must note that even though there’s huge profit potential in derivatives there’s an equal or more probability of losing. It is important to have extremely good knowledge about the stock market, technical analysis and derivatives, to trade in the derivatives market. There’s a lot more to learn about derivatives and their various types, mainly Futures and Options. I am very excited and thrilled to share that my most awaited course on Futures & Options is releasing tomorrow. Make sure you check it out here to learn many more interesting concepts and strategies in the most fun and simplified manner. Until next time!




